
Passing through the network of networks that you already know is one of my greatest hobbies yesterday I found one infographic made by Yerro Agency (agency dedicated to editing, proofreading and writing) where all the formats in which we can find an eBook are shown, explained in a very correct and detailed way.
In the infographic, whose text we have placed just below it so that everyone can read it comfortably, we will find all the formats of digital books so that none of us will ever have a doubt about this sometimes so complicated and complicated topic. dense.
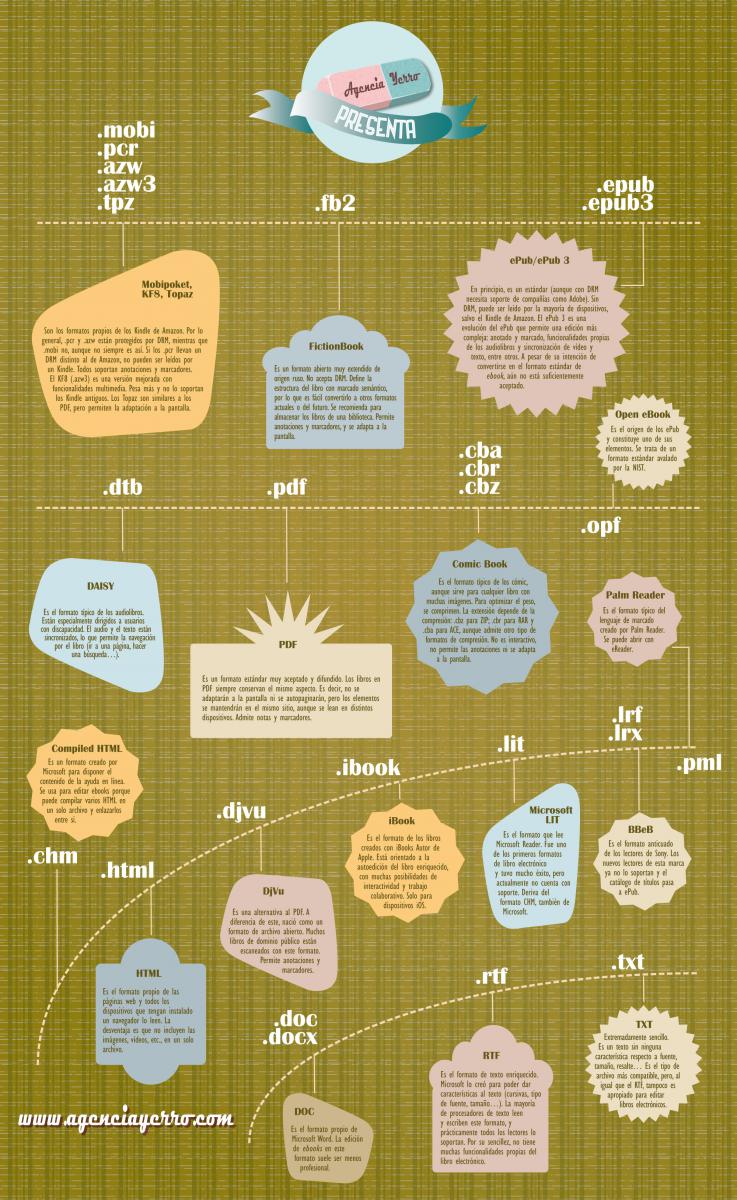
- Mobipoket, KF8, Topaz (.mobi, .pcr, .azw, .azw3, .tpz). They are formats typical of the Amazon Kindle. Typically .pcr and .azw are DRM protected while .mobi is not, although this is not always the case. If the .pcr have a different DRM than Amazon, they cannot be read by a Kindle. All support annotations and bookmarks. The KF8 (.azw3) is an improved version with multimedia functionalities. It weighs more and is not supported by older Kindle. Topaz are similar to PDF, but allow adaptation to the screen.
- FictionBook (.fb2). It is a very widespread open format of Russian origin. It does not accept DRM. It defines the structure of the book with semantic markup, so it is easy to convert to other current or future formats. It is recommended for storing books in a library. It allows annotations and bookmarks, and it adapts to the screen.
- ePub / ePub3 (.epub, .epub3). In principle, it is a standard (although with DRM you need support from companies like Adobe). Without DRM, it can be read by most devices, except for the Amazon Kindle. The ePub 3 is an evolution of the ePub that allows a more complex edition: annotated and marked, functionalities typical of audiobooks and video and text synchronization, among others. Despite its intention to become the standard ebook format, it is still not sufficiently accepted.
- Daisy (.dbt). It is the typical format for audiobooks. They are especially aimed at users with disabilities. The audio and the text are synchronized, which allows navigation through the book (go to a page, do a search ...).
- PDF (.pdf). It is a widely accepted and widespread standard format. PDF books always look the same. That is, they will not adapt to the screen or self-paginate. but the items will stay in the same place, even if they are read on different devices. Supports notes and bookmarks.
- Comic Book (.cba, .cbr, .cbz). It is the typical format of the comics, although it works for any book with many images. To optimize weight, they are compressed. The extension depends on the compression: .cbz for ZIP; .cbr for RAR and .cba for ACE, although it supports other types of compression formats. It is not interactive, does not allow annotations or does not fit the screen.
- Open eBook (.opf). It is the origin of the ePub and constitutes one of its elements. It is a standard format endorsed by NIST.
- PalmReader (.pml). It is the typical format of the markup language created by Palm Reader. It can be opened with eReader.
- BBeB (.lrf, .lrx). It is the outdated format of Sony readers. The new readers of this brand no longer support it and the catalog of titles goes to ePub.
- Microsoft LIT (.lit). It is the format that Microsoft Reader reads. It was one of the first e-book formats and was very successful, but is not currently supported. It is derived from the CHM format, also from Microsoft.
- iBook (.ibook). It is the format of books created with Apple Author iBooks. It is aimed at self-publishing the enriched book, with many possibilities for interactivity and collaborative work. Only for iOS devices.
- DjVu (.djvu). It is an alternative to PDF. Unlike this, it was born as an open file format. Many public domain books are scanned in this format. Allows annotations and bookmarks.
- HTML (.html). It is the proper format of web pages and all devices that have a browser installed read it. The disadvantage is that they do not include the images, videos, etc., in a single file.
- Compiled HTML (.chm). It is a format created by Microsoft to provide the content of the online help. It is used for editing ebooks because it can compile multiple HTML into a single file and link them together.
- txt (.txt). Extremely simple. It is a text without any characteristics regarding font, size, highlight ... It is the most compatible file type, but, like RTF, it is not suitable for editing electronic books.
- RTF (.rtf). It is the rich text format. Microsoft created it to be able to give characteristics to the text (italics. Font type, size ...). Most word processors read and write this format, and almost all readers support it. Due to its simplicity, it does not have many features of the electronic book.
- DOC (.doc, .docx). It is the proprietary format of Microsoft Word. Editing ebooks in this format is often less professional.
Did you know that there were so many different eBook formats?.
Source - agencyyerro.com communitybaratz.com